Walsh Company manufactures and sells one product The followi
Walsh Company manufactures and sells one product. The following information pertains to each of the company’s first two years of operations: Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing: Direct materials $ 23 Direct labor $ 16 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 4 Variable selling and administrative $ 3 Fixed costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 320,000 Fixed selling and administrative expenses $ 50,000 During its first year of operations, Walsh produced 50,000 units and sold 40,000 units. During its second year of operations, it produced 40,000 units and sold 50,000 units. The selling price of the company’s product is $56 per unit. Required: 1. Assume the company uses variable costing: a. Compute the unit product cost for Year 1 and Year 2. b. Prepare an income statement for Year 1 and Year 2. 2. Assume the company uses absorption costing: a. Compute the unit product cost for Year 1 and Year 2. b. Prepare an income statement for Year 1 and Year 2. 3. Reconcile the difference between variable costing and absorption costing net operating income in Year 1.
Solution
Answer
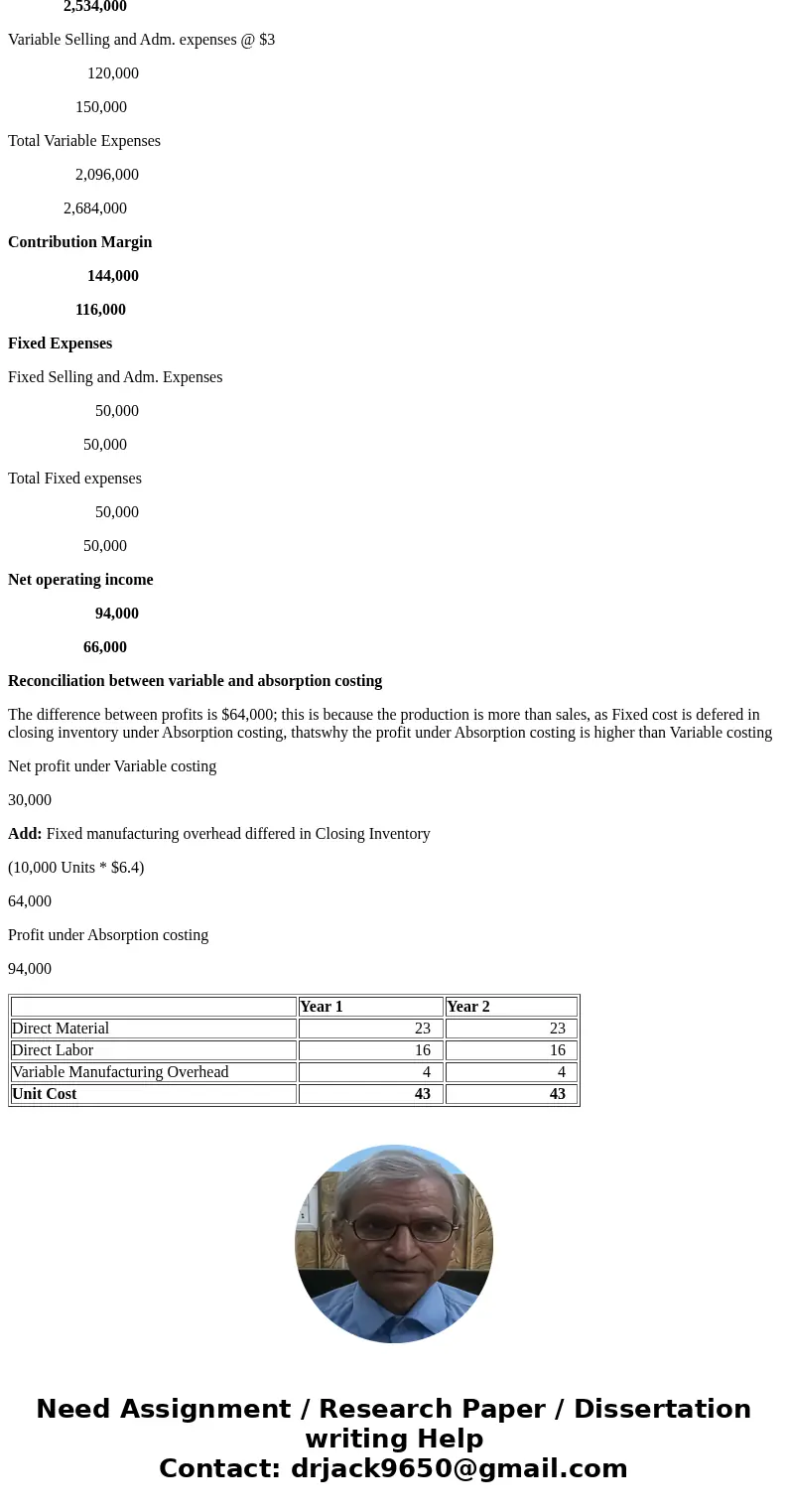
Under Variable Costing
Year 1
Year 2
Direct Material
23
23
Direct Labor
16
16
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
4
4
Unit Cost
43
43
Under Variable Costing, we will include only Variable manufacturing expenses while calculating Unit cost
Income Statement
Sales
2,240,000
2,800,000
Variable Expenses
Cost of Goods Sold
Opening Inventory
-
430,000 (10,000 units *$43)
Add: Cost of Goods Manufactured
2,150,000 (50,000 units *$43)
1,720,000 (40,000 units *$43)
Less: Closing Inventory
430,000 (10,000 units *$43)
-
Cost of Goods Sold
1,720,000
2,150,000
Variable Selling and Adm. expenses @ $3
120,000
150,000
Total Variable Expenses
1,840,000
2,300,000
Contribution Margin
400,000
500,000
Fixed Expenses
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead
320,000
320,000
Fixed Selling and Adm. Expenses
50,000
50,000
Total Fixed expenses
370,000
370,000
Net operating income
30,000
130,000
Under Absorption Costing
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead per unit = Fixed Manufacturing Overhead / No. of Unit Produced
While calculating Unit cost under Absorption costing, we will include Fixed Manufacturing overhead per unit while calculating Unit Cost.
Year 1
Year 2
Direct Material
23
23
Direct Labor
16
16
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
4
4
Fixed Manufacturing overhead
6.4 ($320,000 / 50,000 Units)
8 ($320,000 / 40,000 Units)
Unit Cost
49.4
51
Income Statement
Sales
2,240,000
2,800,000
Variable Expenses
Cost of Goods Sold
Opening Inventory
-
494,000 (10,000 units *$49.4)
Add: Cost of Goods Manufactured
2,470,000 (50,000 units *$49.4)
2,040,000 (40,000 units *$51)
Less: Closing Inventory
494,000 (10,000 units *$49.4)
-
Cost of Goods Sold
1,976,000
2,534,000
Variable Selling and Adm. expenses @ $3
120,000
150,000
Total Variable Expenses
2,096,000
2,684,000
Contribution Margin
144,000
116,000
Fixed Expenses
Fixed Selling and Adm. Expenses
50,000
50,000
Total Fixed expenses
50,000
50,000
Net operating income
94,000
66,000
Reconciliation between variable and absorption costing
The difference between profits is $64,000; this is because the production is more than sales, as Fixed cost is defered in closing inventory under Absorption costing, thatswhy the profit under Absorption costing is higher than Variable costing
Net profit under Variable costing
30,000
Add: Fixed manufacturing overhead differed in Closing Inventory
(10,000 Units * $6.4)
64,000
Profit under Absorption costing
94,000
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Direct Material | 23 | 23 |
| Direct Labor | 16 | 16 |
| Variable Manufacturing Overhead | 4 | 4 |
| Unit Cost | 43 | 43 |



 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse