TABLE 191 PROMINENT FEATURES OF SKULLs OF APES AND HUMANS Fe
Solution
Prominent features of skulls of apes and humans
Feature
Apes
Humans
Sagittal crest
On the top of the skull there is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline. Its presence indicates that the jaw muscles are exceptionally strong. Primarily it is for attachment of the temporalis muscle, which is one of the main muscle for chewing.
Sagittal crests are found in robust great apes, and some early hominins
Sagittal crests are found reduced or absent
Brow ridge
This is a bony ridge located just above the eye sockets. The purpose is to strengthen or support the weaker bones of the face (thus reduces vertical stress).
This is large due to the tremendous strain put on the cranium by their temporal (jaw) muscles. Without its support the eye sockets would collapse.
The brow ridge was lost in the path to modern humans
Foramen magnum
This is the hole at the base of the skull from where the spinal cord enters the brain.
It is towards the back of the skull in apes, posture was not fully upright. Thus it is at the rear of the skull in apes
It is at the fulcrum (balance point). The bones of the skull that balance on the vertebra / spine (occipital condyles) also show the same trend. Thus it is exactly at the
center in humans
Prognathism
Pronounced muzzle, the teeth protrudes out from their face.
Present
This is common in early Hominins also,
ABSENT, characterized by Flatter face
Canines
Teeth
The canines of males are considerably larger than females- Sexual dimorphism with thinner enamel
Sharper
And
have thick enamel, this is an adaption for chewing harder or tougher food materials
Inscisors
Teeth
Much larger incisors and also have a gap diastema between the upper incisors and canines
No such gap and are smaller.
Chin
The mandible or Lower jaw
is much larger supporting its food habits
is small and developed to protect a weak point in our less robust skulls.
Arrangement of teeth
more U shaped dental arcade with diastema, a gap.
V shaped dental arcade
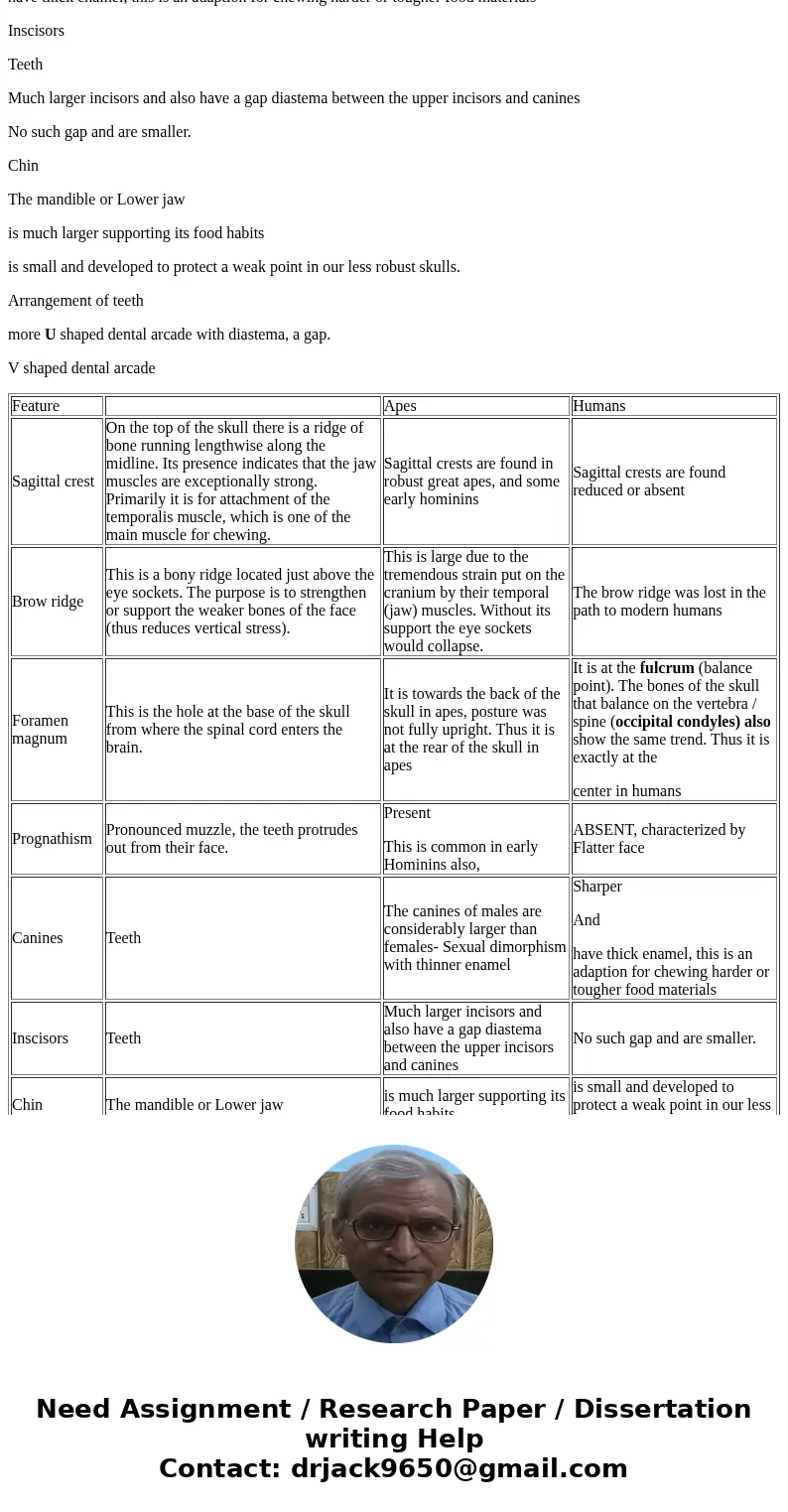
| Feature | Apes | Humans | |
| Sagittal crest | On the top of the skull there is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline. Its presence indicates that the jaw muscles are exceptionally strong. Primarily it is for attachment of the temporalis muscle, which is one of the main muscle for chewing. | Sagittal crests are found in robust great apes, and some early hominins | Sagittal crests are found reduced or absent |
| Brow ridge | This is a bony ridge located just above the eye sockets. The purpose is to strengthen or support the weaker bones of the face (thus reduces vertical stress). | This is large due to the tremendous strain put on the cranium by their temporal (jaw) muscles. Without its support the eye sockets would collapse. | The brow ridge was lost in the path to modern humans |
| Foramen magnum | This is the hole at the base of the skull from where the spinal cord enters the brain. | It is towards the back of the skull in apes, posture was not fully upright. Thus it is at the rear of the skull in apes | It is at the fulcrum (balance point). The bones of the skull that balance on the vertebra / spine (occipital condyles) also show the same trend. Thus it is exactly at the center in humans |
| Prognathism | Pronounced muzzle, the teeth protrudes out from their face. | Present This is common in early Hominins also, | ABSENT, characterized by Flatter face |
| Canines | Teeth | The canines of males are considerably larger than females- Sexual dimorphism with thinner enamel | Sharper And have thick enamel, this is an adaption for chewing harder or tougher food materials |
| Inscisors | Teeth | Much larger incisors and also have a gap diastema between the upper incisors and canines | No such gap and are smaller. |
| Chin | The mandible or Lower jaw | is much larger supporting its food habits | is small and developed to protect a weak point in our less robust skulls. |
| Arrangement of teeth | more U shaped dental arcade with diastema, a gap. | V shaped dental arcade |

 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse