Terms A System Concept B A thermodynamic properties of fluid
Solution
1
System
A quantity of matter or region in space choosen for study
2
3
4
5
6
Cv
As dH/dt is Cp so is dU/dt is to
7
8
work
As efficiency is to heat engine, so is coefficient of performance is to
9
10
11
12
13
Quasi static
Process proceeds in such a manner that system remains infinitesimally close to equilibrium
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
friction
A good common source of irreversibility is
21
22
23
24
25
transformaton of energy from one form to another
26
27
28
29
Super critical fluid
A fluid with temperature and pressure above critical point
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
Entropy
A measure of disorderliness from microscopic point of view
38
Compressibility factor
39
40
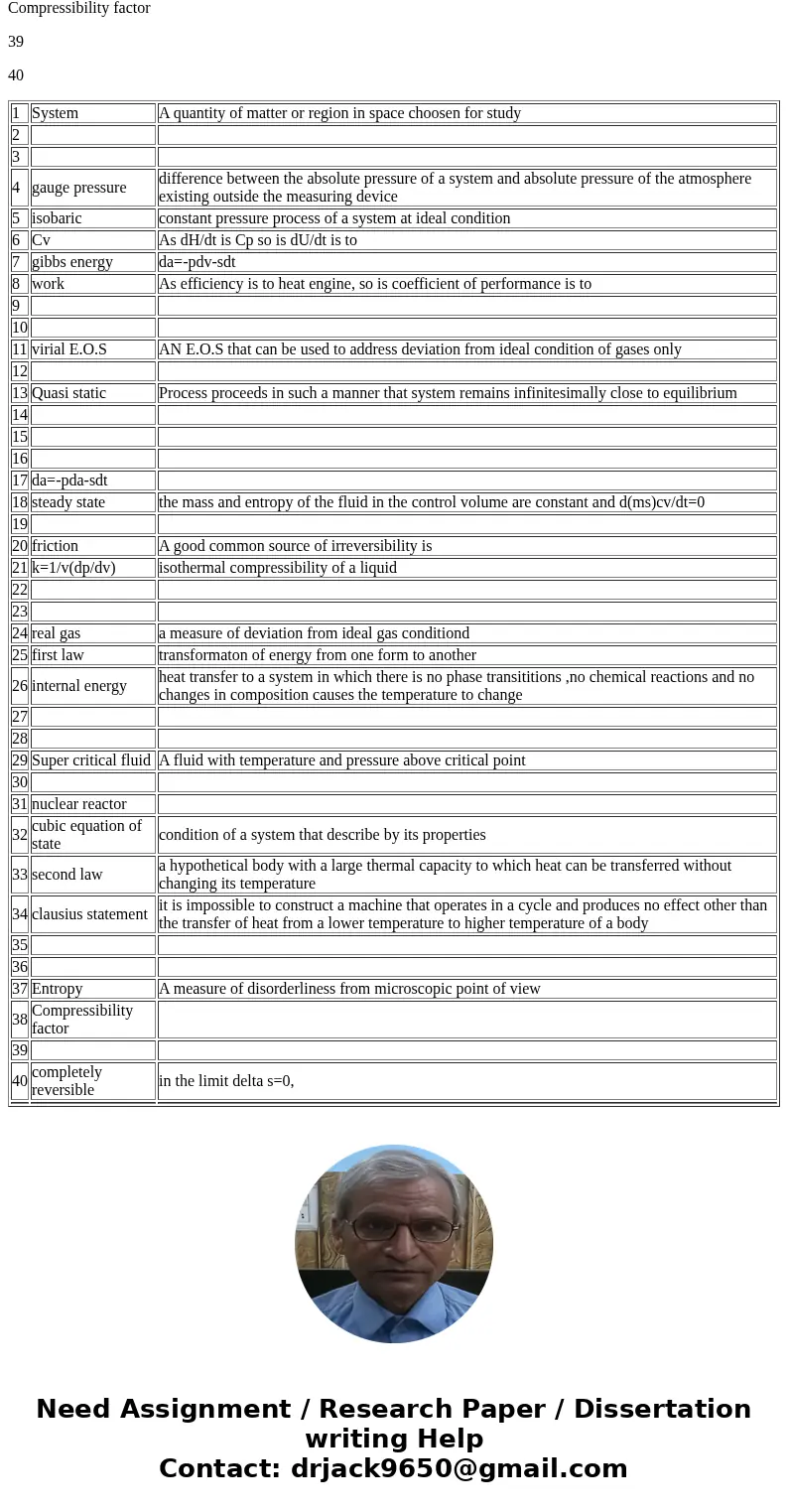
| 1 | System | A quantity of matter or region in space choosen for study |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | gauge pressure | difference between the absolute pressure of a system and absolute pressure of the atmosphere existing outside the measuring device |
| 5 | isobaric | constant pressure process of a system at ideal condition |
| 6 | Cv | As dH/dt is Cp so is dU/dt is to |
| 7 | gibbs energy | da=-pdv-sdt |
| 8 | work | As efficiency is to heat engine, so is coefficient of performance is to |
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | virial E.O.S | AN E.O.S that can be used to address deviation from ideal condition of gases only |
| 12 | ||
| 13 | Quasi static | Process proceeds in such a manner that system remains infinitesimally close to equilibrium |
| 14 | ||
| 15 | ||
| 16 | ||
| 17 | da=-pda-sdt | |
| 18 | steady state | the mass and entropy of the fluid in the control volume are constant and d(ms)cv/dt=0 |
| 19 | ||
| 20 | friction | A good common source of irreversibility is |
| 21 | k=1/v(dp/dv) | isothermal compressibility of a liquid |
| 22 | ||
| 23 | ||
| 24 | real gas | a measure of deviation from ideal gas conditiond |
| 25 | first law | transformaton of energy from one form to another |
| 26 | internal energy | heat transfer to a system in which there is no phase transititions ,no chemical reactions and no changes in composition causes the temperature to change |
| 27 | ||
| 28 | ||
| 29 | Super critical fluid | A fluid with temperature and pressure above critical point |
| 30 | ||
| 31 | nuclear reactor | |
| 32 | cubic equation of state | condition of a system that describe by its properties |
| 33 | second law | a hypothetical body with a large thermal capacity to which heat can be transferred without changing its temperature |
| 34 | clausius statement | it is impossible to construct a machine that operates in a cycle and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a lower temperature to higher temperature of a body |
| 35 | ||
| 36 | ||
| 37 | Entropy | A measure of disorderliness from microscopic point of view |
| 38 | Compressibility factor | |
| 39 | ||
| 40 | completely reversible | in the limit delta s=0, |

 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse