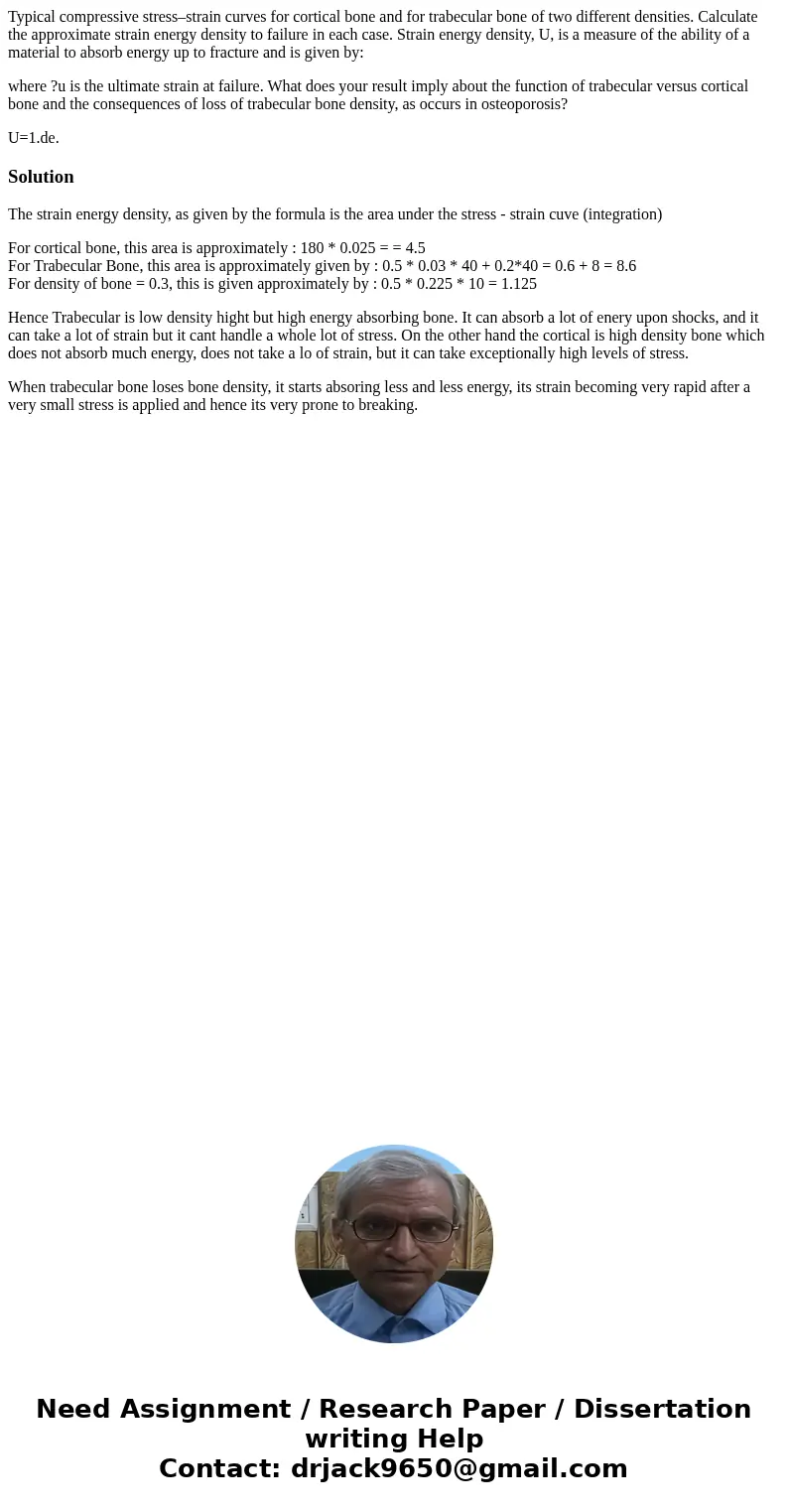
Typical compressive stressstrain curves for cortical bone an
Typical compressive stress–strain curves for cortical bone and for trabecular bone of two different densities. Calculate the approximate strain energy density to failure in each case. Strain energy density, U, is a measure of the ability of a material to absorb energy up to fracture and is given by:
where ?u is the ultimate strain at failure. What does your result imply about the function of trabecular versus cortical bone and the consequences of loss of trabecular bone density, as occurs in osteoporosis?
U=1.de.Solution
The strain energy density, as given by the formula is the area under the stress - strain cuve (integration)
For cortical bone, this area is approximately : 180 * 0.025 = = 4.5
For Trabecular Bone, this area is approximately given by : 0.5 * 0.03 * 40 + 0.2*40 = 0.6 + 8 = 8.6
For density of bone = 0.3, this is given approximately by : 0.5 * 0.225 * 10 = 1.125
Hence Trabecular is low density hight but high energy absorbing bone. It can absorb a lot of enery upon shocks, and it can take a lot of strain but it cant handle a whole lot of stress. On the other hand the cortical is high density bone which does not absorb much energy, does not take a lo of strain, but it can take exceptionally high levels of stress.
When trabecular bone loses bone density, it starts absoring less and less energy, its strain becoming very rapid after a very small stress is applied and hence its very prone to breaking.
 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse