Unit 11Imperfect Competition 1 Identify the three types of i
Unit 11—Imperfect Competition
1) Identify the three types of imperfect competition and list five characteristics of each form of competition
A:
B:
C:
1
2
3
4
5
2) Why are monopolists price-makers while firms in perfect competition are price takers?
Questions 3-5 refer to the following: For many years Keurig held a patent on the design of the K-Cup, which prevented other firms from making pods that would work with Keurig coffee makers. The demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves are drawn below.
3) Find the marginal benefit curve and identify the efficient price and quantity. Why is this combination of price and quantity efficient?
4) What is the price and quantity if Keurig acts as a monopolist?
5) Shade in consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss when Keurig is a monopolist. Does the monopoly increase total surplus or decrease total surplus?
6) Give two reasons why monopolies can make society better off
Multiple choice questions:
1. Which of the following is a characteristic of a monopoly?
a. The firm produces a product that has many close substitutes.
b. There are barriers to entry in the market.
c. The firm has no control over price.
d. The firm\'s demand curve is perfectly elastic.
2. Assume someone organizes all bread producers in the nation into a monopoly.
Which of the following will occur?
a. Consumer surplus decreases and deadweight losses are created
b. Deadweight losses are created and economic profit increases
c. Consumer surplus decreases and economic profit increases
d. Consumer surplus decreases, deadweight losses are created, and economic profit increases
3. A monopolist can make an economic profit in the long run because of
a. the many firms that produce in the market.
b. product homogeneity.
c. barriers to entry.
d. the perfectly inelastic demand curve that it faces.
| A: | B: | C: | |
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 |
Solution
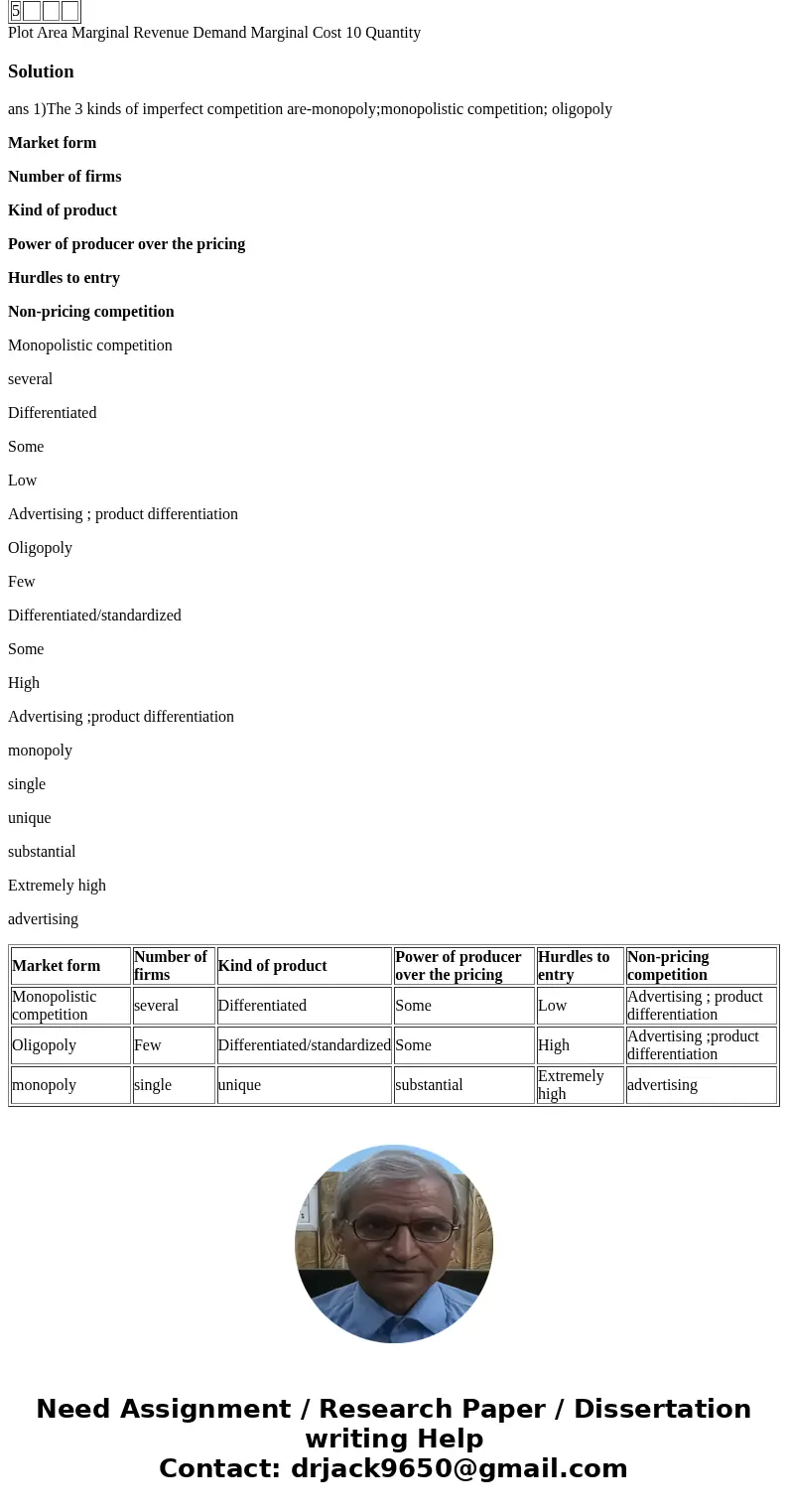
ans 1)The 3 kinds of imperfect competition are-monopoly;monopolistic competition; oligopoly
Market form
Number of firms
Kind of product
Power of producer over the pricing
Hurdles to entry
Non-pricing competition
Monopolistic competition
several
Differentiated
Some
Low
Advertising ; product differentiation
Oligopoly
Few
Differentiated/standardized
Some
High
Advertising ;product differentiation
monopoly
single
unique
substantial
Extremely high
advertising
| Market form | Number of firms | Kind of product | Power of producer over the pricing | Hurdles to entry | Non-pricing competition |
| Monopolistic competition | several | Differentiated | Some | Low | Advertising ; product differentiation |
| Oligopoly | Few | Differentiated/standardized | Some | High | Advertising ;product differentiation |
| monopoly | single | unique | substantial | Extremely high | advertising |

 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse