Objectives 1 using indirect addressing 2 passing parameters
Objectives:
1. using indirect addressing
2. passing parameters
3. generating “random” numbers
4. working with arrays
Description:
Write and test a MASM (assembly language) program to perform the following tasks:
1. Introduce the program.
2. Get a user request in the range [min = 10 .. max = 200].
3. Generate request random integers in the range [lo = 100 .. hi = 999], storing them in consecutive elements of an array.
4. Display the list of integers before sorting, 10 numbers per line.
5. Sort the list in descending order (i.e., largest first).
6. Calculate and display the median value, rounded to the nearest integer.
7. Display the sorted list, 10 numbers per line.
Requirements:
1. The title, programmer\'s name, and brief instructions must be displayed on the screen.
2. The program must validate the user’s request.
3. min, max, lo, and hi must be declared and used as global constants. Strings may be declared as global variables or constants.
4. The program must be constructed using procedures. At least the following procedures are required:
A. main
B. introduction
C. get data {parameters: request (reference)}
D. fill array {parameters: request (value), array (reference)}
E. sort list {parameters: array (reference), request (value)}
i. exchange elements (for most sorting algorithms): {parameters: array[i] (reference), array[j] (reference), where i and j are the indexes of elements to be exchanged}
F. display median {parameters: array (reference), request (value)}
G. display list {parameters: array (reference), request (value), title (reference)}
5. Parameters must be passed by value or by reference on the system stack as noted above.
6. There must be just one procedure to display the list. This procedure must be called twice: once to display the unsorted list, and once to display the sorted list.
7. Procedures (except main) should not reference .data segment variables by name. request, array, and titles for the sorted/unsorted lists should be declared in the .data segment, but procedures must use them as parameters. Procedures may use local variables when appropriate. Global constants are OK.
8. The program must use appropriate addressing modes for array elements.
9. The two lists must be identified when they are displayed (use the title parameter for the display procedure).
10. The program must be fully documented. This includes a complete header block for the program and for each procedure, and a comment outline to explain each section of code.
11. The code and the output must be well-formatted.
12. Submit your text code file (.asm) to Canvas by the due date.
Extra Credit (Be sure to describe your extras in the program header block):
1. Display the numbers ordered by column instead of by row.
2. Use a recursive sorting algorithm (e.g., Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Heap Sort, etc.).
3. Implement the program using floating-point numbers and the floating-point processor.
4. Generate the numbers into a file; then read the file into the array.
5. Others?
To ensure you receive credit for any extra credit options you did, you must add one print statement to your program output PER EXTRA CREDIT which describes the extra credit you chose to work on. You will not receive extra credit points unless you do this. The statement must be formatted as follows...
--Program Intro--
**EC: DESCRIPTION
--Program prompts, etc—
Notes:
1. The Irvine library provides procedures for generating random numbers. Call Randomize once at the beginning of the program (to set up so you don\'t get the same sequence every time), and call RandomRange to get a pseudo-random number. (See the documentation in Lecture slides.)
2. The Selection Sort is probably the easiest sorting algorithm to implement. Here is a version of the descending order algorithm, where request is the number of array elements being sorted, and exchange is the code to exchange two elements of array:
for(k=0; k<request-1; k++) {
i = k;
for(j=k+1; j<request; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[i])
i = j;
}
exchange(array[k], array[i]);
}
3. The median is calculated after the array is sorted. It is the \"middle\" element of the sorted list. If the number of elements is even, the median is the average of the middle two elements (may be rounded).
Example (user input is in italics):
Sorting Random Integers Programmed by Road Runner
This program generates random numbers in the range [100 .. 999],
displays the original list, sorts the list, and calculates the
median value. Finally, it displays the list sorted in descending order.
How many numbers should be generated? [10 .. 200]: 9
Invalid input
How many numbers should be generated? [10 .. 200]: 16
The unsorted random numbers:
680 329 279 846 123 101 427 913 255 736
431 545 984 391 626 803
The median is 488.
The sorted list:
984 913 846 803 736 680 626 545 431 427
391 329 279 255 123 101
Solution
INCLUDE Irvine32.inc
.data
myName BYTE \"chegs \", 0
programTitle BYTE\"Programming Assignment \", 0
instructions BYTE \"Please enter two numbers, and I\'ll show you the sum, difference, product, quotient, and remainder.\", 0
prompt_1 BYTE \"First Number: \", 0
prompt_2 BYTE \"Second Number: \", 0
firstNumber DWORD ? ; integer entered by user
secondNumber DWORD ? ; second integer entered by user
.
goodBye BYTE \"Goodbye\",0
equalsString BYTE \" = \", 0
sum DWORD ?
sumString BYTE \" + \",0
difference DWORD ?
differenceString BYTE \" - \",0
product DWORD ?
productString BYTE \" * \",0
quotient DWORD ?
quotientString BYTE \" / \",0
remainder DWORD ?
remainderString BYTE \" remainder \",0
;
.code
main PROC
; Introduction
; Get The Data
; This section gets the first and second number and jumps if the user\'s second number is greater than the first number
; the program will still allow them to loop even if they enter a second number that is greater than the first.
mov edx, OFFSET instructions
call WriteString
call CrLf
; get firstNumber
top:
mov edx, OFFSET prompt_1
call WriteString
call ReadInt
mov firstNumber, eax
; get secondNumber
mov edx, OFFSET prompt_2
call WriteString
call ReadInt
mov secondNumber, eax
; **EC: Jump if second number greater than first
mov eax, secondNumber
cmp eax, firstNumber
jg Warning
jle Calculate
Warning:
mov edx, OFFSET EC1warn
call WriteString
call CrLf
jg JumpToLoop ; jump if secondNumber > firstNumber
Calculate: ; Calculate Required Values
; sum
mov eax, firstNumber
add eax, secondNumber
mov sum, eax
; difference
mov eax, firstNumber
sub eax, secondNumber
mov difference, eax
; product
mov eax, firstNumber
mov ebx, secondNumber
mul ebx
mov product, eax
; quotient
mov edx, 0
mov eax, firstNumber
cdq
mov ebx, secondNumber
cdq
div ebx
mov quotient, eax
mov remainder, edx
; Display Results
; sum results
mov eax, firstNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET sumString
call WriteString
mov eax, secondNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET equalsString
call WriteString
mov eax, sum
call WriteDec
call CrLf
; difference results
mov eax, firstNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET differenceString
call WriteString
mov eax, secondNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET equalsString
call WriteString
mov eax, difference
call WriteDec
call CrLf
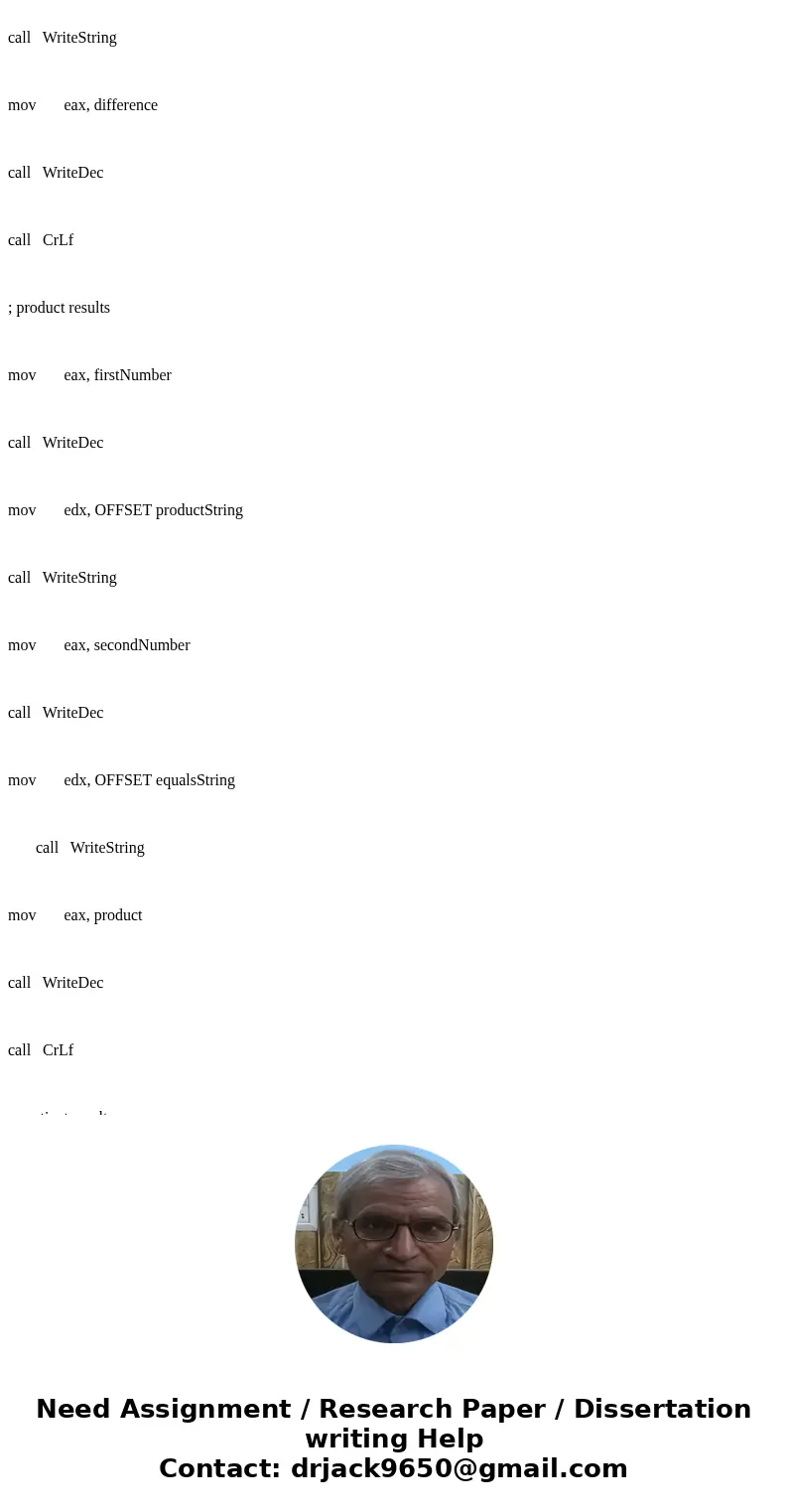
; product results
mov eax, firstNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET productString
call WriteString
mov eax, secondNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET equalsString
call WriteString
mov eax, product
call WriteDec
call CrLf
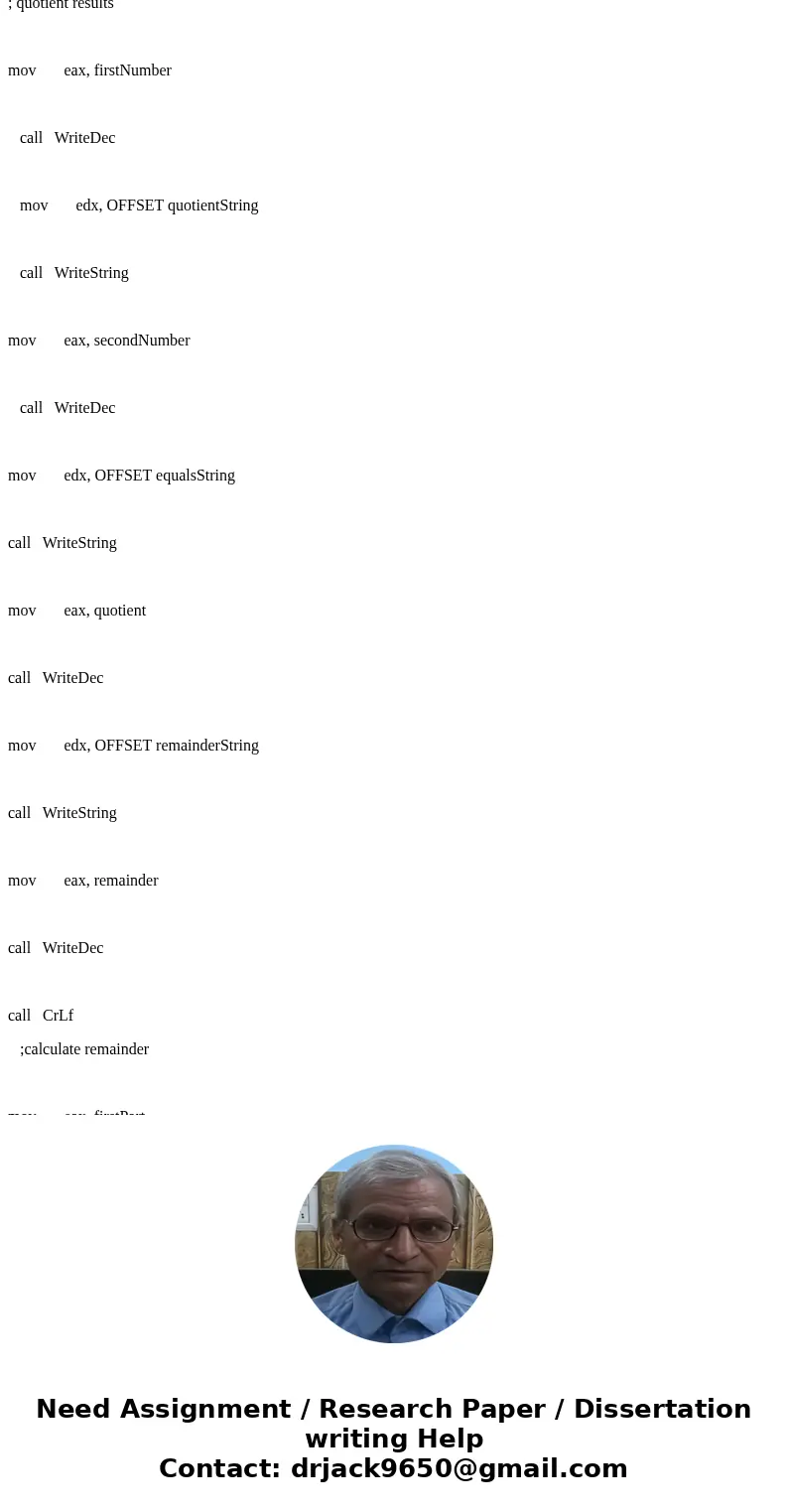
; quotient results
mov eax, firstNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET quotientString
call WriteString
mov eax, secondNumber
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET equalsString
call WriteString
mov eax, quotient
call WriteDec
mov edx, OFFSET remainderString
call WriteString
mov eax, remainder
call WriteDec
call CrLf
;calculate remainder
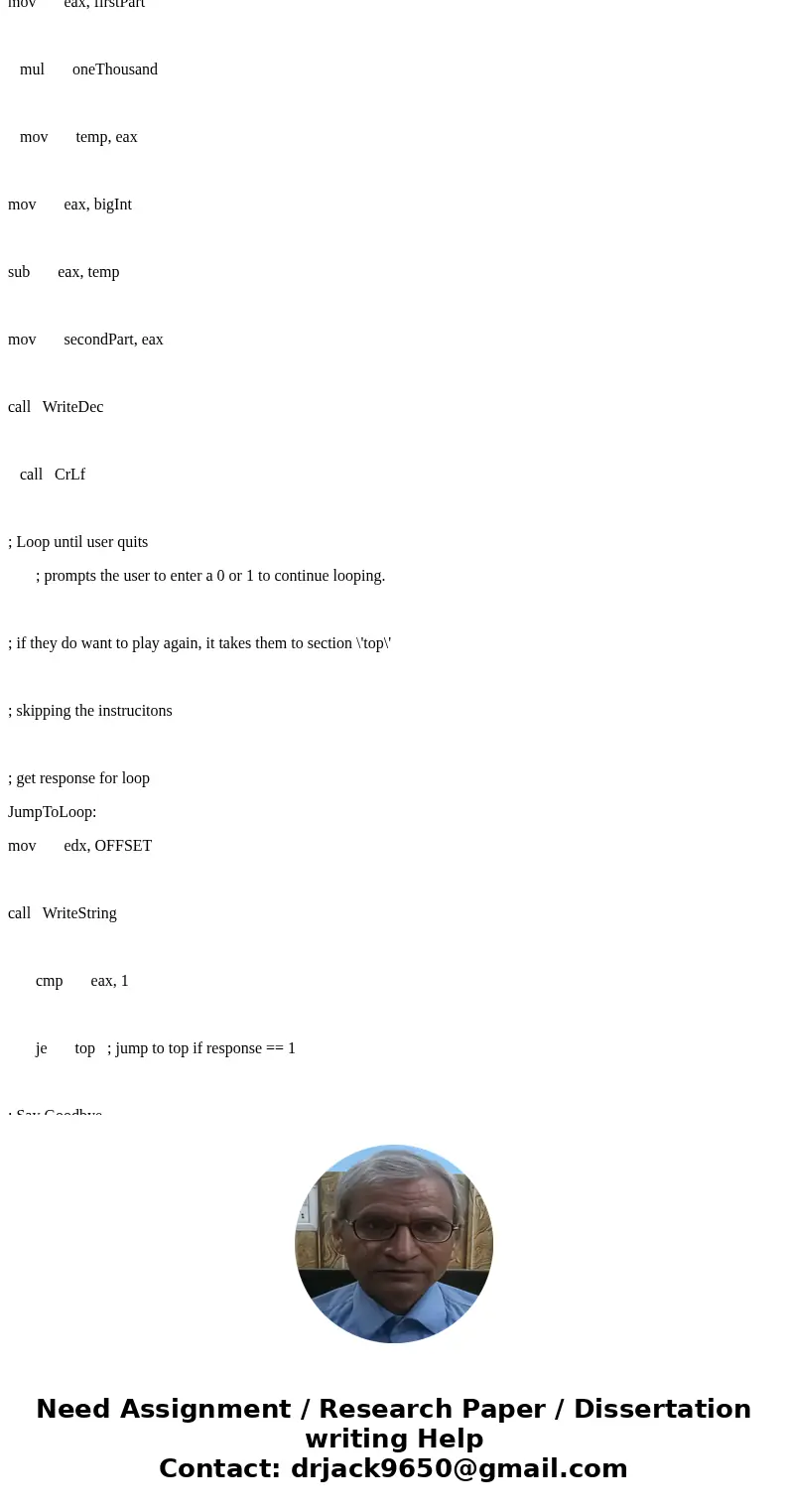
mov eax, firstPart
mul oneThousand
mov temp, eax
mov eax, bigInt
sub eax, temp
mov secondPart, eax
call WriteDec
call CrLf
; Loop until user quits
; prompts the user to enter a 0 or 1 to continue looping.
; if they do want to play again, it takes them to section \'top\'
; skipping the instrucitons
; get response for loop
JumpToLoop:
mov edx, OFFSET
call WriteString
cmp eax, 1
je top ; jump to top if response == 1
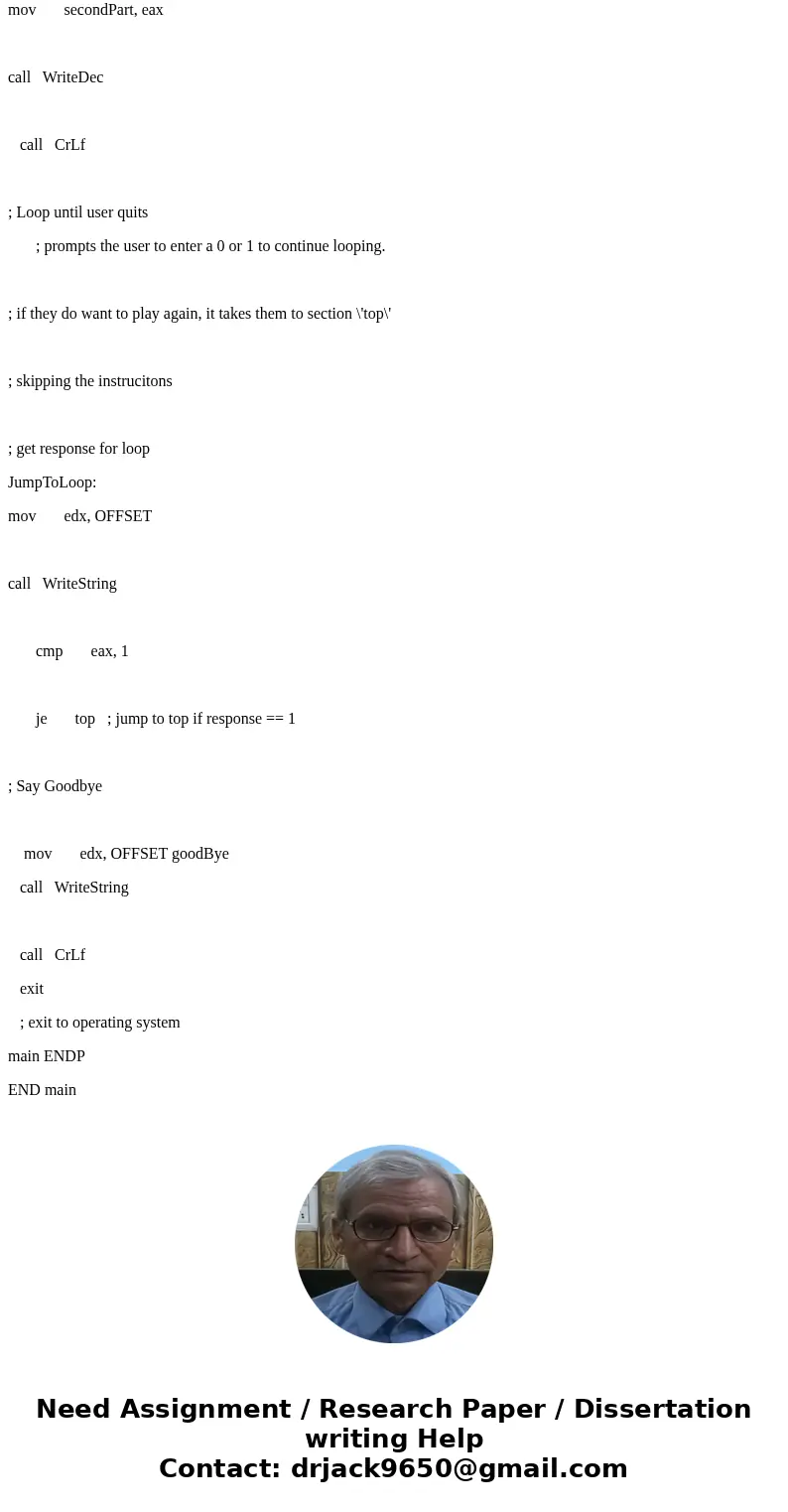
; Say Goodbye
mov edx, OFFSET goodBye
call WriteString
call CrLf
exit
; exit to operating system
main ENDP
END main






 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse