problem 9 Compute Kelsons shortrun supply curve for its prod
problem 9
Compute Kelson\'s shortrun supply curve for its product. ame manufacturer of electronics products has just developed a handheld co mputer for producing these computers on a monthly basis. Also Following is the cost schedule inciu (based on previous market research). included is a schedule of prices and quantities that the firm believes it will be able to Q (Thousands)Price MR AVC AC $1,650 1,570 1,490 1,410 1,330 1,250 1,170 1,090 1,010 930 850 $1,570 1,410 1,250 1,090 930 770 610 450 290 130 $1,281 $2,281 1,134 1,009 1,634 1,342.33 $1,281 987 906 1,156 825 1,025 766 729 714 721 750 4 597 932.67 871.86 839 832.11 850 6 471 507 609 9 10 1,011 a. What price should the firm charge if it wants to maximize its profits in the short run: b. What arguments can be made for charging a price higher than this price? If a higher price is indeed established, what amount would you recommend? Explain. What arguments can be made for charging a lower price than the prof If a lower price is indeed established, what amount would you recommend? Explain. c. Tha manufacrer f high-quality flatbed scanners is trying to decide what price to set forSolution
ANSWER:
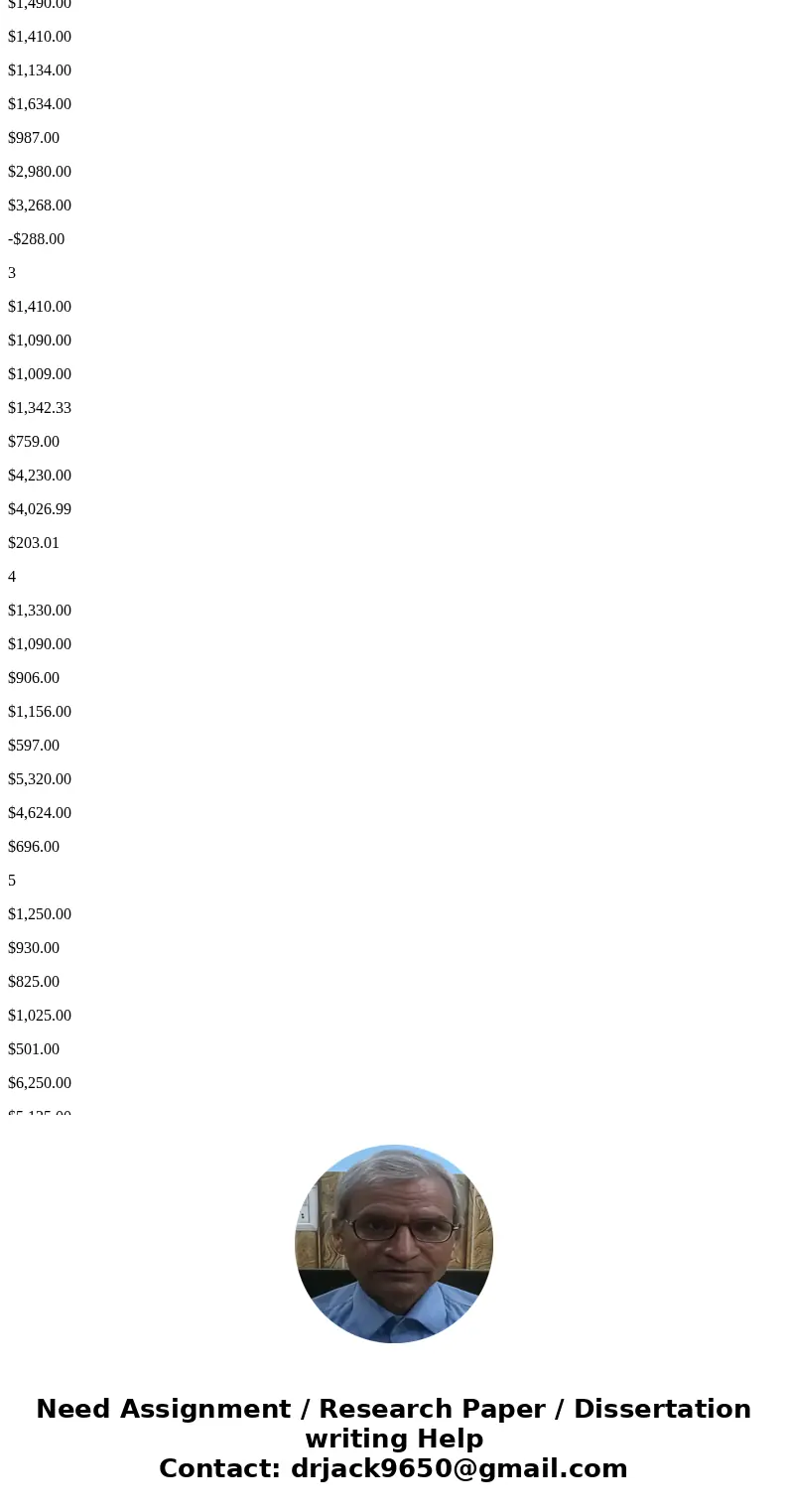
1) The profit maximization price is computed where MR=MC. In the below table there is no such price level. Now if we assume that the firm cannot sell a fraction of the product then will sell an additional unit where MR>MC and stop when MC exceeds MR. In the below table at Q=7, MR > MC however at Q=8, MC exceeds MR, thus the profit maximizing price is $1,090
Q
Price
MR
AVC
AC
MC
TR
Total Cost
Profit
0
$1,650.00
1
$1,570.00
$1,570.00
$1,281.00
$2,281.00
$1,281.00
$1,570.00
$2,281.00
-$711.00
2
$1,490.00
$1,410.00
$1,134.00
$1,634.00
$987.00
$2,980.00
$3,268.00
-$288.00
3
$1,410.00
$1,090.00
$1,009.00
$1,342.33
$759.00
$4,230.00
$4,026.99
$203.01
4
$1,330.00
$1,090.00
$906.00
$1,156.00
$597.00
$5,320.00
$4,624.00
$696.00
5
$1,250.00
$930.00
$825.00
$1,025.00
$501.00
$6,250.00
$5,125.00
$1,125.00
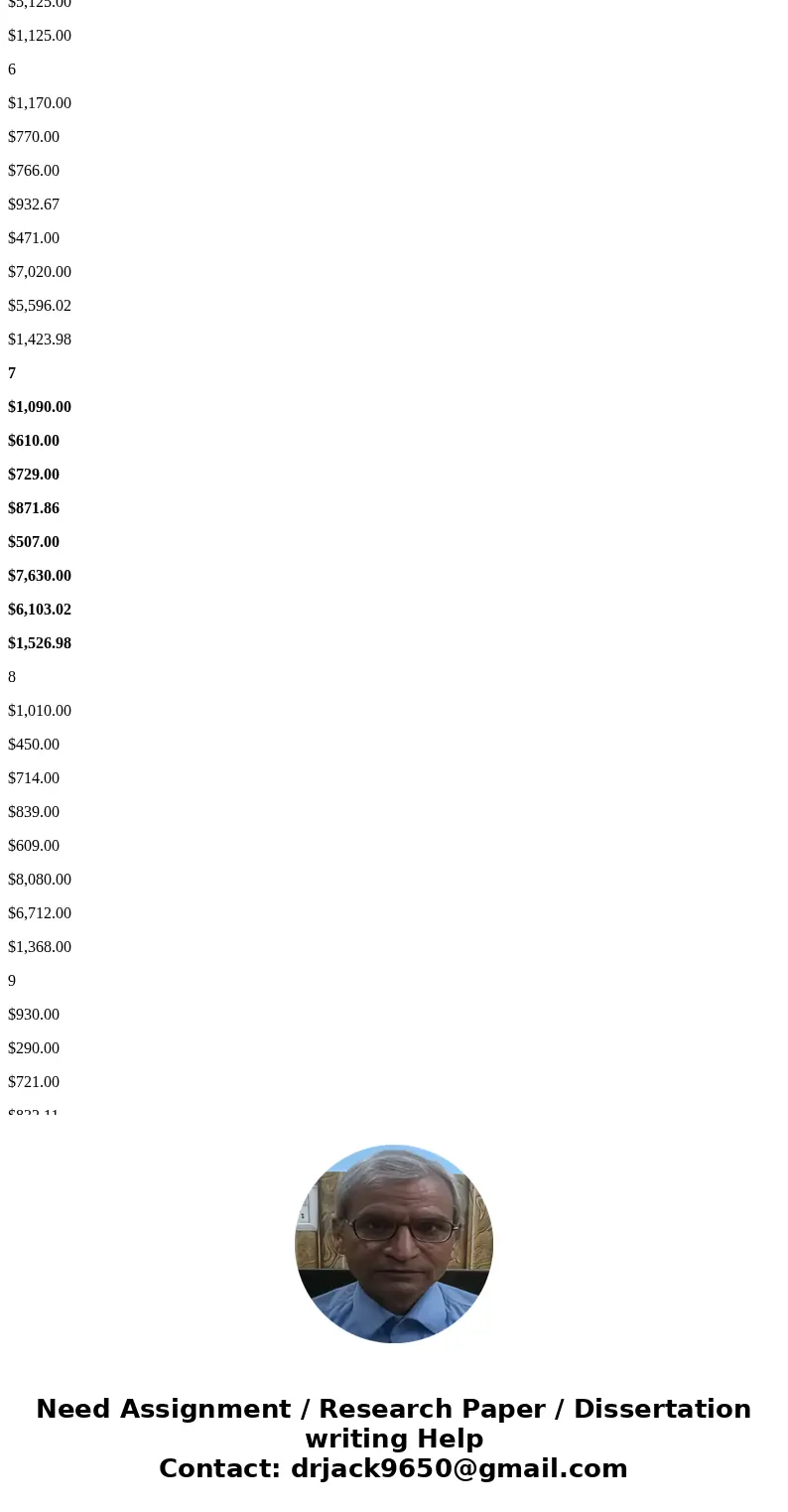
6
$1,170.00
$770.00
$766.00
$932.67
$471.00
$7,020.00
$5,596.02
$1,423.98
7
$1,090.00
$610.00
$729.00
$871.86
$507.00
$7,630.00
$6,103.02
$1,526.98
8
$1,010.00
$450.00
$714.00
$839.00
$609.00
$8,080.00
$6,712.00
$1,368.00
9
$930.00
$290.00
$721.00
$832.11
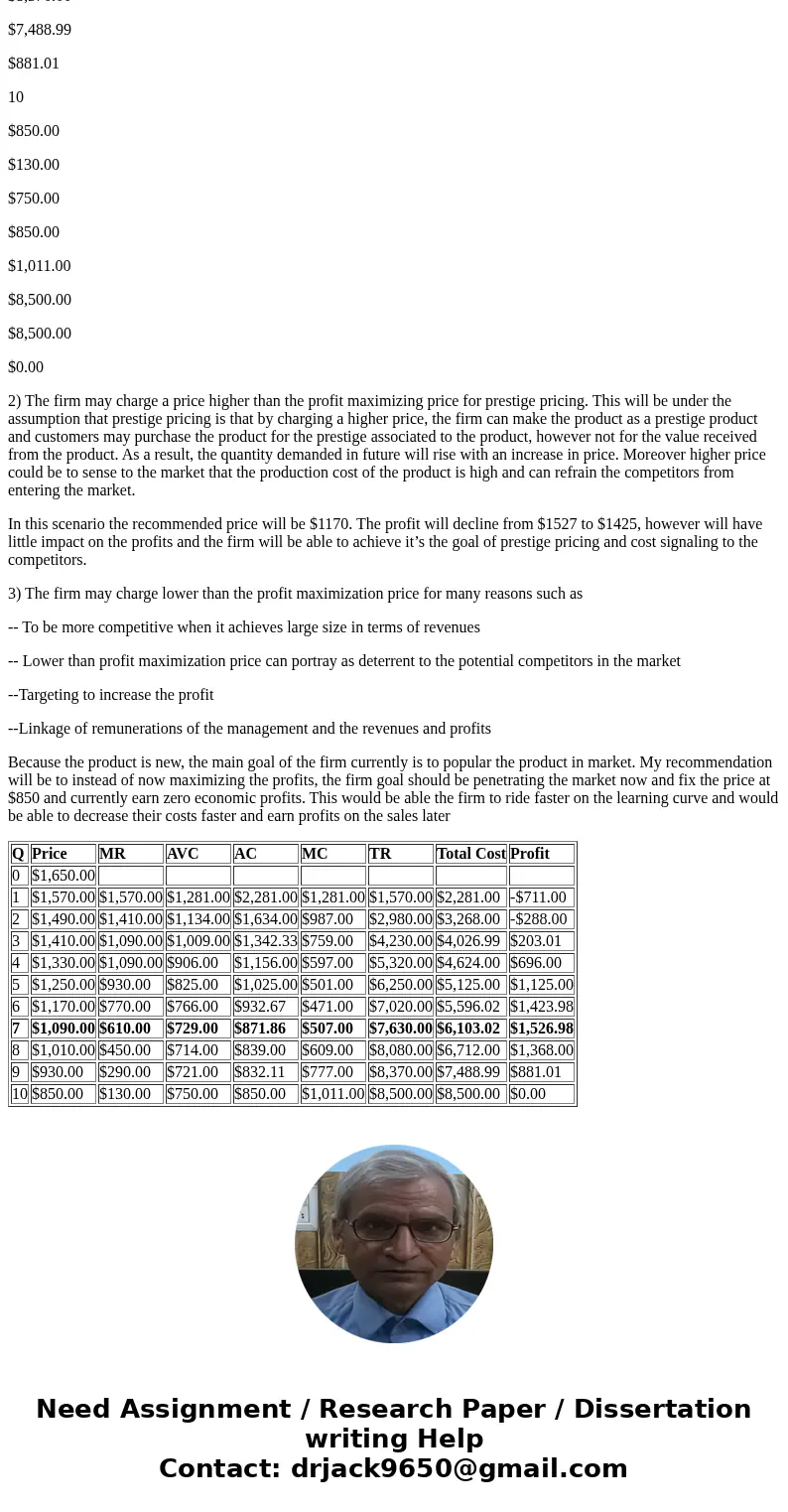
$777.00
$8,370.00
$7,488.99
$881.01
10
$850.00
$130.00
$750.00
$850.00
$1,011.00
$8,500.00
$8,500.00
$0.00
2) The firm may charge a price higher than the profit maximizing price for prestige pricing. This will be under the assumption that prestige pricing is that by charging a higher price, the firm can make the product as a prestige product and customers may purchase the product for the prestige associated to the product, however not for the value received from the product. As a result, the quantity demanded in future will rise with an increase in price. Moreover higher price could be to sense to the market that the production cost of the product is high and can refrain the competitors from entering the market.
In this scenario the recommended price will be $1170. The profit will decline from $1527 to $1425, however will have little impact on the profits and the firm will be able to achieve it’s the goal of prestige pricing and cost signaling to the competitors.
3) The firm may charge lower than the profit maximization price for many reasons such as
-- To be more competitive when it achieves large size in terms of revenues
-- Lower than profit maximization price can portray as deterrent to the potential competitors in the market
--Targeting to increase the profit
--Linkage of remunerations of the management and the revenues and profits
Because the product is new, the main goal of the firm currently is to popular the product in market. My recommendation will be to instead of now maximizing the profits, the firm goal should be penetrating the market now and fix the price at $850 and currently earn zero economic profits. This would be able the firm to ride faster on the learning curve and would be able to decrease their costs faster and earn profits on the sales later
| Q | Price | MR | AVC | AC | MC | TR | Total Cost | Profit |
| 0 | $1,650.00 | |||||||
| 1 | $1,570.00 | $1,570.00 | $1,281.00 | $2,281.00 | $1,281.00 | $1,570.00 | $2,281.00 | -$711.00 |
| 2 | $1,490.00 | $1,410.00 | $1,134.00 | $1,634.00 | $987.00 | $2,980.00 | $3,268.00 | -$288.00 |
| 3 | $1,410.00 | $1,090.00 | $1,009.00 | $1,342.33 | $759.00 | $4,230.00 | $4,026.99 | $203.01 |
| 4 | $1,330.00 | $1,090.00 | $906.00 | $1,156.00 | $597.00 | $5,320.00 | $4,624.00 | $696.00 |
| 5 | $1,250.00 | $930.00 | $825.00 | $1,025.00 | $501.00 | $6,250.00 | $5,125.00 | $1,125.00 |
| 6 | $1,170.00 | $770.00 | $766.00 | $932.67 | $471.00 | $7,020.00 | $5,596.02 | $1,423.98 |
| 7 | $1,090.00 | $610.00 | $729.00 | $871.86 | $507.00 | $7,630.00 | $6,103.02 | $1,526.98 |
| 8 | $1,010.00 | $450.00 | $714.00 | $839.00 | $609.00 | $8,080.00 | $6,712.00 | $1,368.00 |
| 9 | $930.00 | $290.00 | $721.00 | $832.11 | $777.00 | $8,370.00 | $7,488.99 | $881.01 |
| 10 | $850.00 | $130.00 | $750.00 | $850.00 | $1,011.00 | $8,500.00 | $8,500.00 | $0.00 |


 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse