Investigate the following features or constructs as they per
Solution
A mini-project which has condition statements and a function can be added to show the remaining features as well.
Example program:
Customers = {
\'Alex\': 5000,
\'Florence\': 2300,
\'Carol\': 4500,
\'Nelson\': 1000,
\'Michele\': 300
}
rewards = {}
def assign_rewards(Cust):
for k,v in Cust.items():
rewards[k]=v*.01
return
def print_rewards():
for rk, rv in rewards.items():
print (rk, rv)
return
assign_rewards(Customers)
print_rewards()
Output:
Features of the language in this example:
Here dictionary and looping through all the elements of the dictionary is shown.
Unlike other programming languages, the variable declaration is not needed, bracket open and close are not needed for the loop and indention serves as a good feature to identify the statements in the loop. In other languages indention is used only for readability and it is optional.
The complex operations are done with a single statement as seen in this example. Here based on how much each customer has spent, rewards are calculated and printed.
assign_rewards() and print_rewards() are 2 functions.
Use of functions and indention is demonstrated as well.
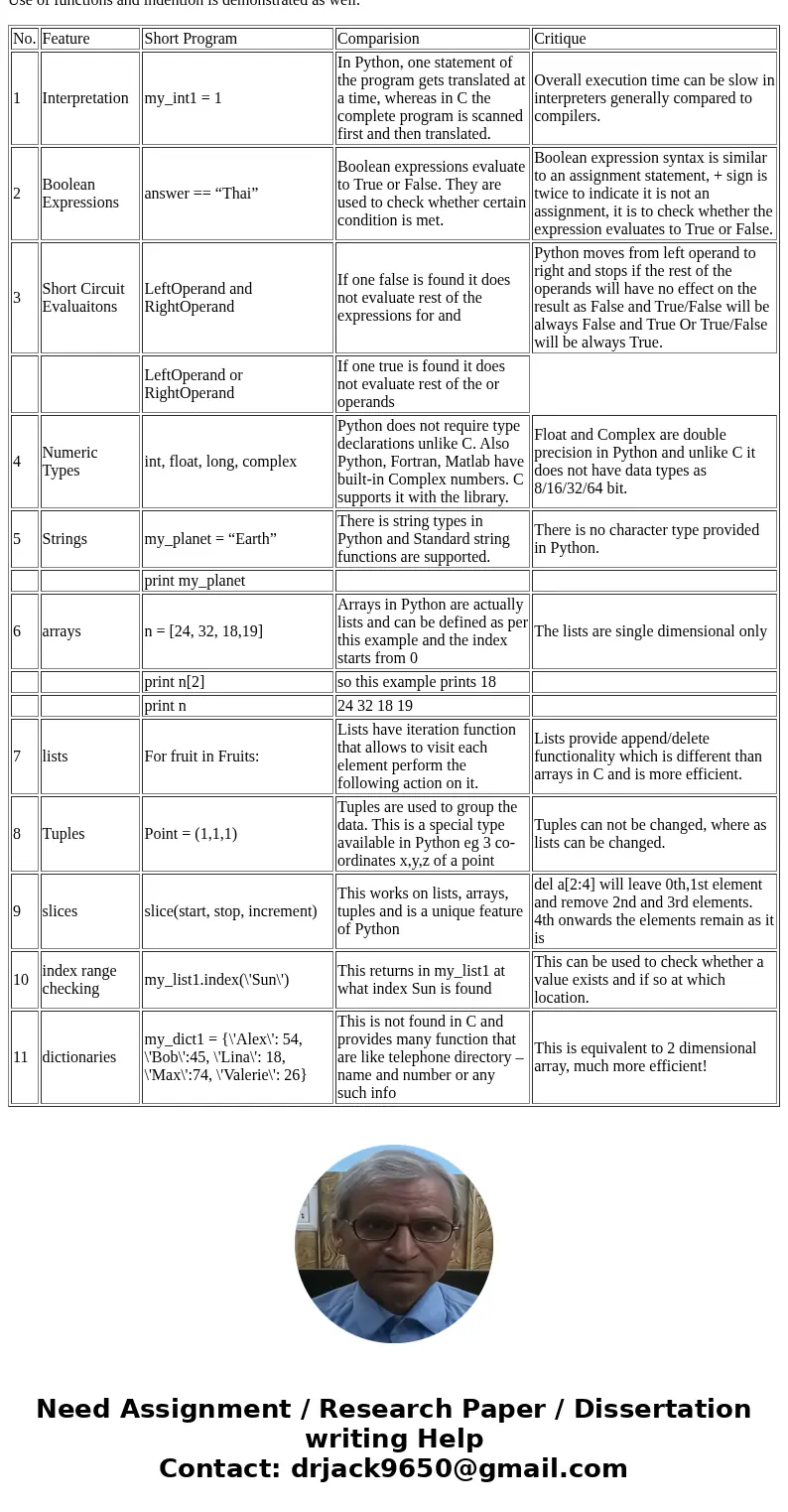
| No. | Feature | Short Program | Comparision | Critique |
| 1 | Interpretation | my_int1 = 1 | In Python, one statement of the program gets translated at a time, whereas in C the complete program is scanned first and then translated. | Overall execution time can be slow in interpreters generally compared to compilers. |
| 2 | Boolean Expressions | answer == “Thai” | Boolean expressions evaluate to True or False. They are used to check whether certain condition is met. | Boolean expression syntax is similar to an assignment statement, + sign is twice to indicate it is not an assignment, it is to check whether the expression evaluates to True or False. |
| 3 | Short Circuit Evaluaitons | LeftOperand and RightOperand | If one false is found it does not evaluate rest of the expressions for and | Python moves from left operand to right and stops if the rest of the operands will have no effect on the result as False and True/False will be always False and True Or True/False will be always True. |
| LeftOperand or RightOperand | If one true is found it does not evaluate rest of the or operands | |||
| 4 | Numeric Types | int, float, long, complex | Python does not require type declarations unlike C. Also Python, Fortran, Matlab have built-in Complex numbers. C supports it with the library. | Float and Complex are double precision in Python and unlike C it does not have data types as 8/16/32/64 bit. |
| 5 | Strings | my_planet = “Earth” | There is string types in Python and Standard string functions are supported. | There is no character type provided in Python. |
| print my_planet | ||||
| 6 | arrays | n = [24, 32, 18,19] | Arrays in Python are actually lists and can be defined as per this example and the index starts from 0 | The lists are single dimensional only |
| print n[2] | so this example prints 18 | |||
| print n | 24 32 18 19 | |||
| 7 | lists | For fruit in Fruits: | Lists have iteration function that allows to visit each element perform the following action on it. | Lists provide append/delete functionality which is different than arrays in C and is more efficient. |
| 8 | Tuples | Point = (1,1,1) | Tuples are used to group the data. This is a special type available in Python eg 3 co-ordinates x,y,z of a point | Tuples can not be changed, where as lists can be changed. |
| 9 | slices | slice(start, stop, increment) | This works on lists, arrays, tuples and is a unique feature of Python | del a[2:4] will leave 0th,1st element and remove 2nd and 3rd elements. 4th onwards the elements remain as it is |
| 10 | index range checking | my_list1.index(\'Sun\') | This returns in my_list1 at what index Sun is found | This can be used to check whether a value exists and if so at which location. |
| 11 | dictionaries | my_dict1 = {\'Alex\': 54, \'Bob\':45, \'Lina\': 18, \'Max\':74, \'Valerie\': 26} | This is not found in C and provides many function that are like telephone directory – name and number or any such info | This is equivalent to 2 dimensional array, much more efficient! |

 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse