Acid dissociation is an equilibrium Set up an ice table for
Solution
Solution
pH = 6.53 = -log [H+]
[H+] = 10-6.53 = 2.95 x 10-7 M
At equilibrium [H3O+] = 2.95 x 10-7 M = ([A-]
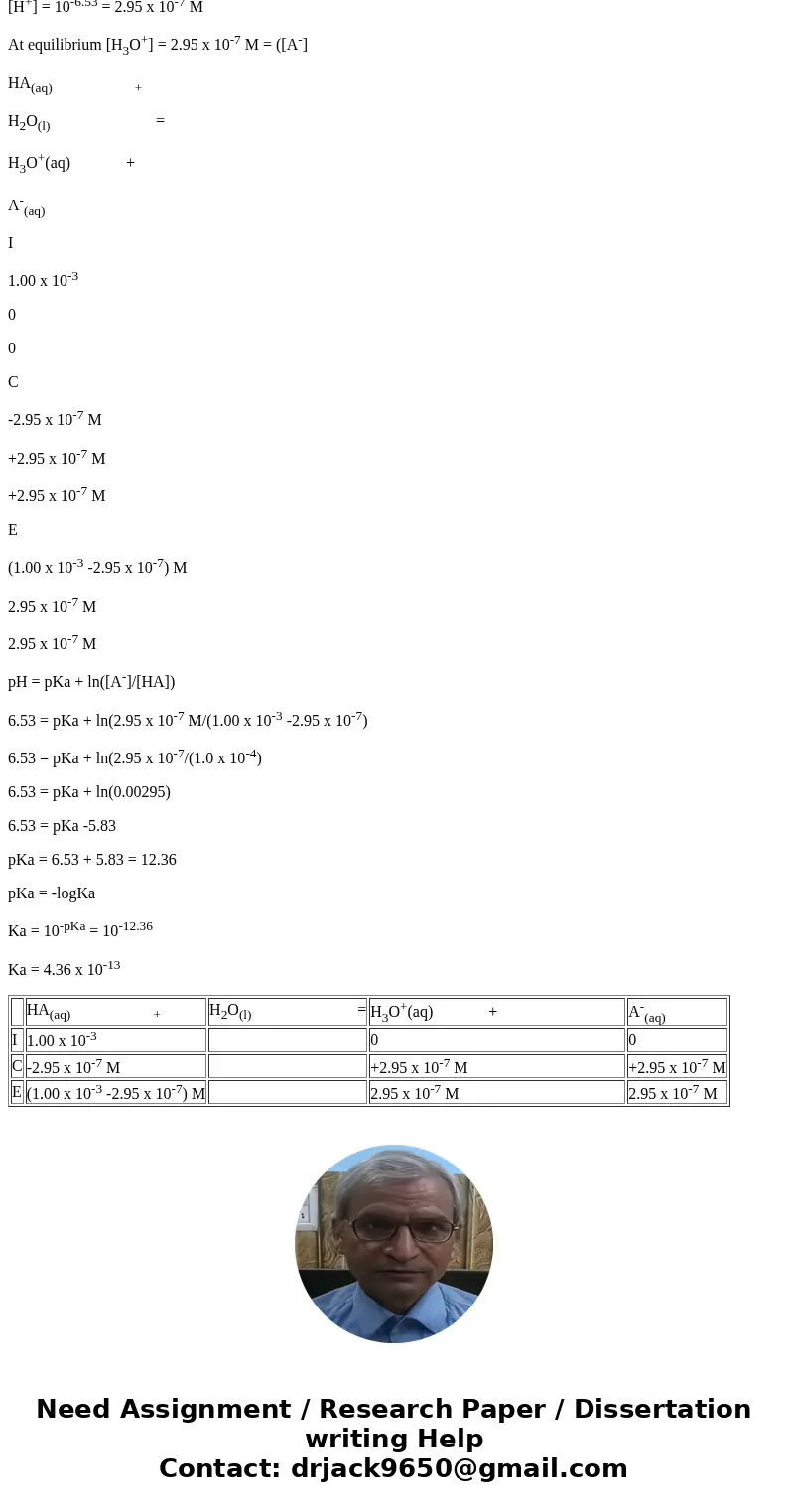
HA(aq) +
H2O(l) =
H3O+(aq) +
A-(aq)
I
1.00 x 10-3
0
0
C
-2.95 x 10-7 M
+2.95 x 10-7 M
+2.95 x 10-7 M
E
(1.00 x 10-3 -2.95 x 10-7) M
2.95 x 10-7 M
2.95 x 10-7 M
pH = pKa + ln([A-]/[HA])
6.53 = pKa + ln(2.95 x 10-7 M/(1.00 x 10-3 -2.95 x 10-7)
6.53 = pKa + ln(2.95 x 10-7/(1.0 x 10-4)
6.53 = pKa + ln(0.00295)
6.53 = pKa -5.83
pKa = 6.53 + 5.83 = 12.36
pKa = -logKa
Ka = 10-pKa = 10-12.36
Ka = 4.36 x 10-13
| HA(aq) + | H2O(l) = | H3O+(aq) + | A-(aq) | |
| I | 1.00 x 10-3 | 0 | 0 | |
| C | -2.95 x 10-7 M | +2.95 x 10-7 M | +2.95 x 10-7 M | |
| E | (1.00 x 10-3 -2.95 x 10-7) M | 2.95 x 10-7 M | 2.95 x 10-7 M |
 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse