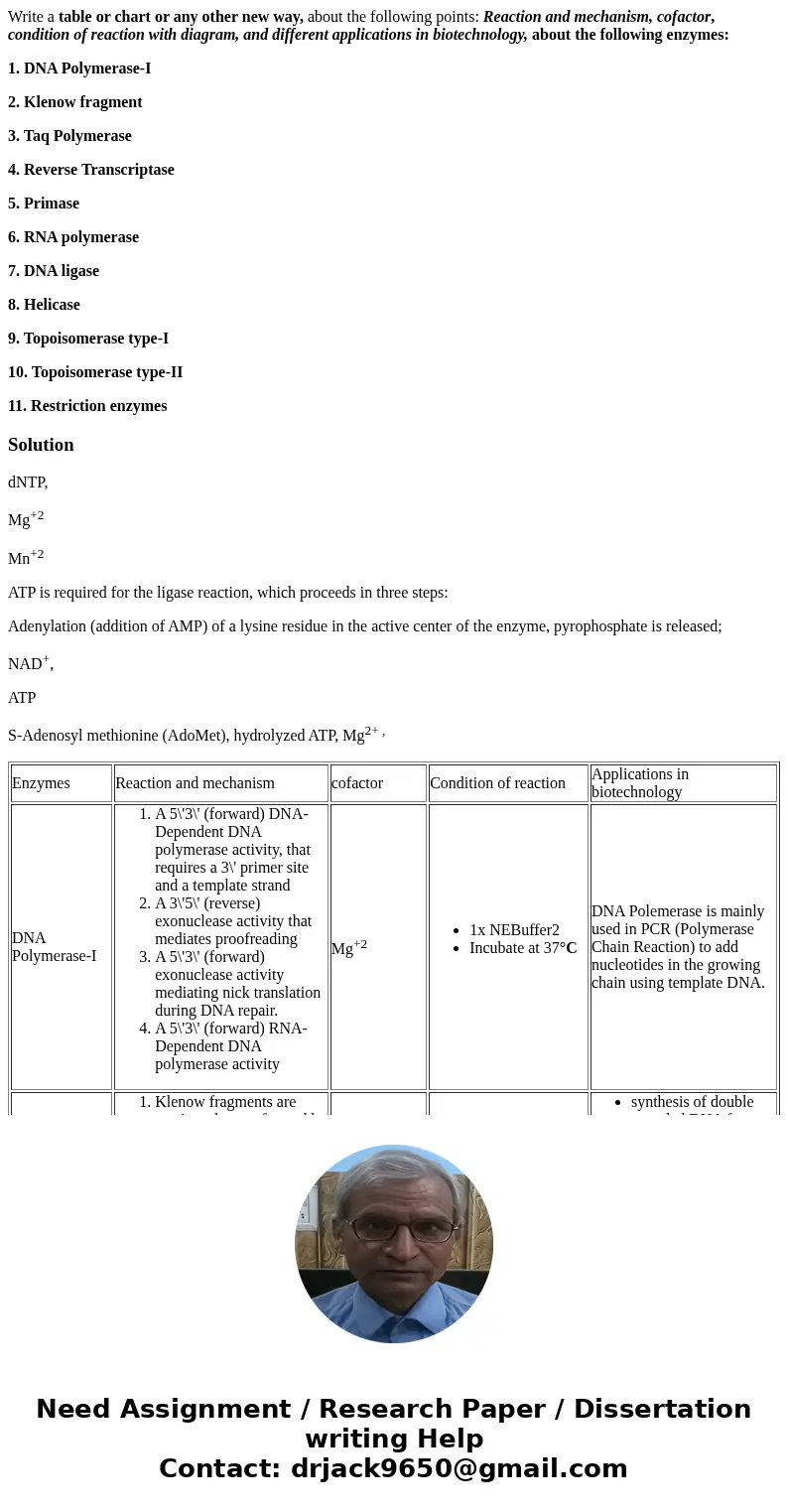
| Enzymes | Reaction and mechanism | cofactor | Condition of reaction | Applications in biotechnology |
| DNA Polymerase-I | - A 5\'3\' (forward) DNA-Dependent DNA polymerase activity, that requires a 3\' primer site and a template strand
- A 3\'5\' (reverse) exonuclease activity that mediates proofreading
- A 5\'3\' (forward) exonuclease activity mediating nick translation during DNA repair.
- A 5\'3\' (forward) RNA-Dependent DNA polymerase activity
| Mg+2 | - 1x NEBuffer2
- Incubate at 37°C
| DNA Polemerase is mainly used in PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to add nucleotides in the growing chain using template DNA. |
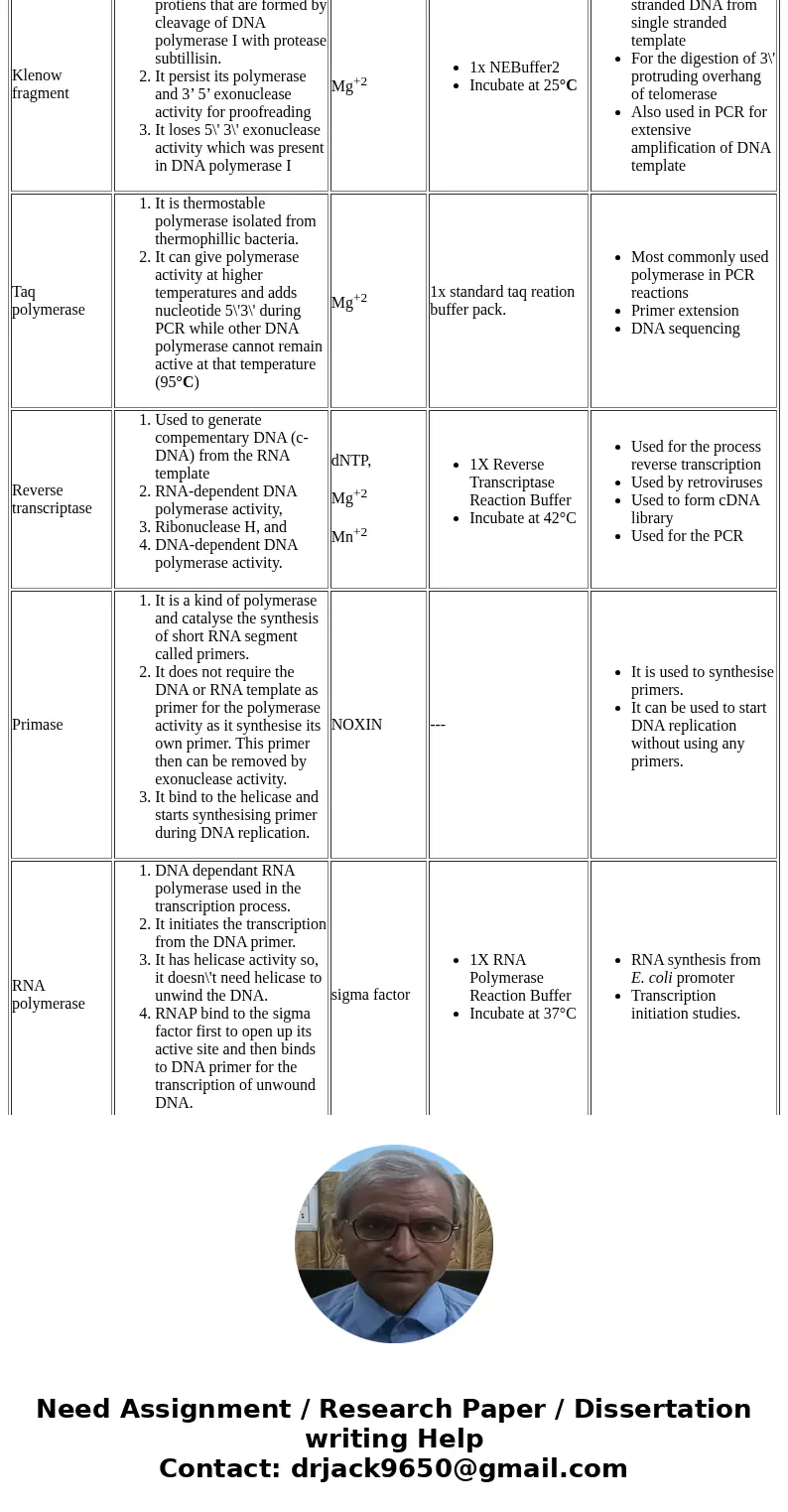
| Klenow fragment | - Klenow fragments are protiens that are formed by cleavage of DNA polymerase I with protease subtillisin.
- It persist its polymerase and 3’ 5’ exonuclease activity for proofreading
- It loses 5\' 3\' exonuclease activity which was present in DNA polymerase I
| Mg+2 | - 1x NEBuffer2
- Incubate at 25°C
| - synthesis of double stranded DNA from single stranded template
- For the digestion of 3\' protruding overhang of telomerase
- Also used in PCR for extensive amplification of DNA template
|
| Taq polymerase | - It is thermostable polymerase isolated from thermophillic bacteria.
- It can give polymerase activity at higher temperatures and adds nucleotide 5\'3\' during PCR while other DNA polymerase cannot remain active at that temperature (95°C)
| Mg+2 | 1x standard taq reation buffer pack. | - Most commonly used polymerase in PCR reactions
- Primer extension
- DNA sequencing
|
| Reverse transcriptase | - Used to generate compementary DNA (c-DNA) from the RNA template
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity,
- Ribonuclease H, and
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity.
| dNTP, Mg+2 Mn+2 | - 1X Reverse Transcriptase Reaction Buffer
- Incubate at 42°C
| - Used for the process reverse transcription
- Used by retroviruses
- Used to form cDNA library
- Used for the PCR
|
| Primase | - It is a kind of polymerase and catalyse the synthesis of short RNA segment called primers.
- It does not require the DNA or RNA template as primer for the polymerase activity as it synthesise its own primer. This primer then can be removed by exonuclease activity.
- It bind to the helicase and starts synthesising primer during DNA replication.
| NOXIN | --- | - It is used to synthesise primers.
- It can be used to start DNA replication without using any primers.
|
| RNA polymerase | - DNA dependant RNA polymerase used in the transcription process.
- It initiates the transcription from the DNA primer.
- It has helicase activity so, it doesn\'t need helicase to unwind the DNA.
- RNAP bind to the sigma factor first to open up its active site and then binds to DNA primer for the transcription of unwound DNA.
| sigma factor | - 1X RNA Polymerase Reaction Buffer
- Incubate at 37°C
| - RNA synthesis from E. coli promoter
- Transcription initiation studies.
|
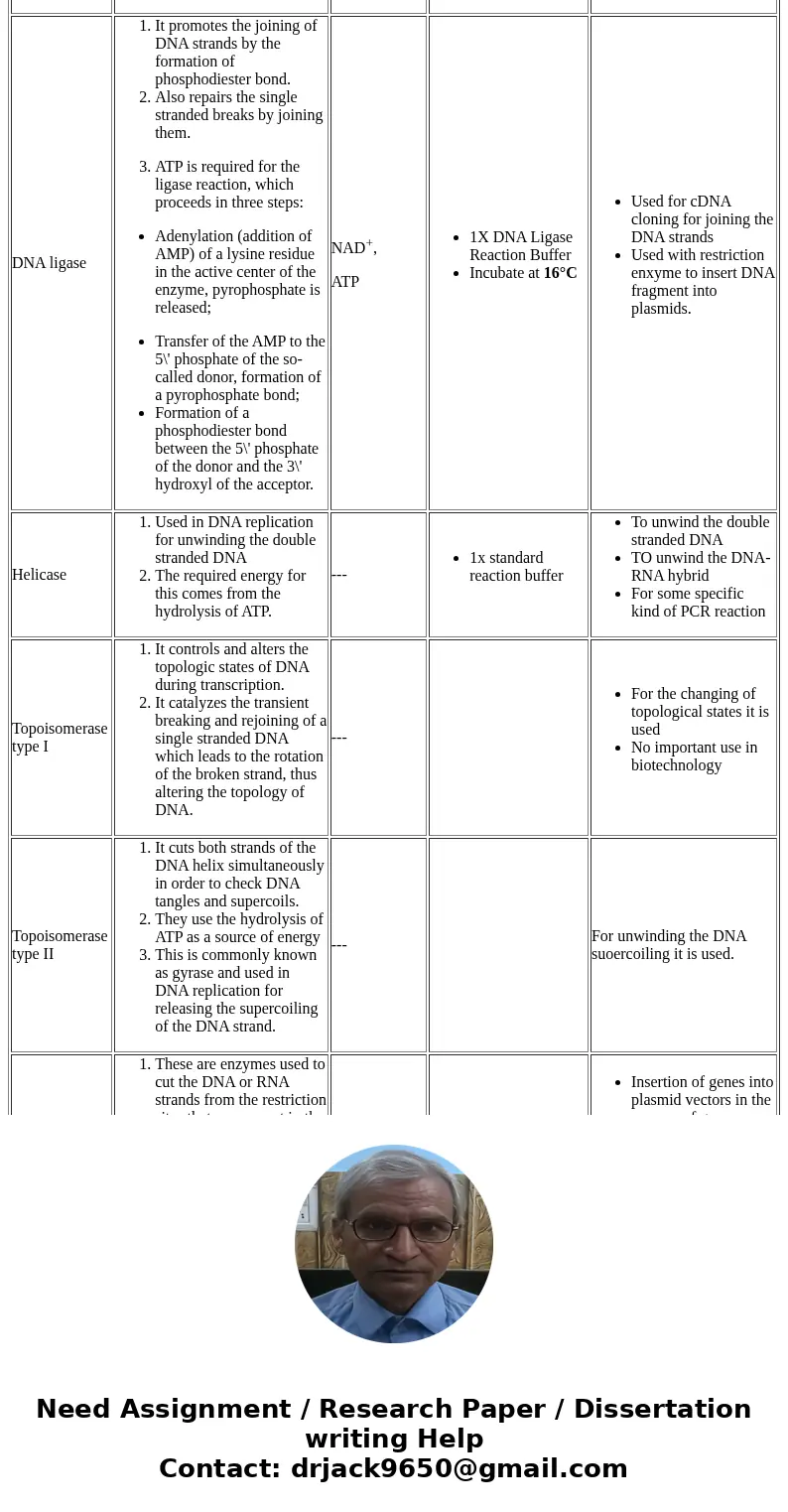
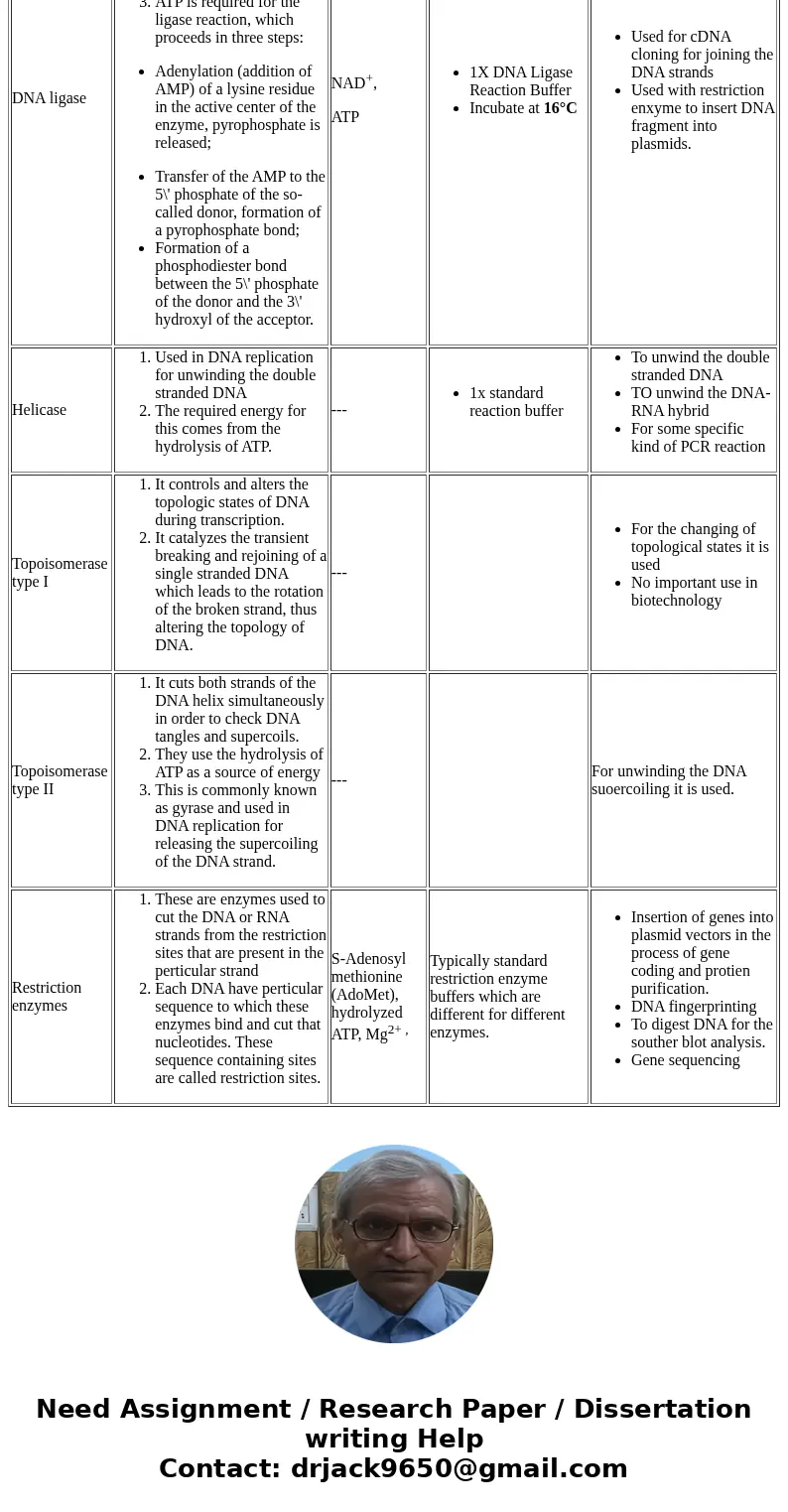
| DNA ligase | - It promotes the joining of DNA strands by the formation of phosphodiester bond.
- Also repairs the single stranded breaks by joining them.
-
ATP is required for the ligase reaction, which proceeds in three steps: | NAD+, ATP | - 1X DNA Ligase Reaction Buffer
- Incubate at 16°C
| - Used for cDNA cloning for joining the DNA strands
- Used with restriction enxyme to insert DNA fragment into plasmids.
|
| Helicase | - Used in DNA replication for unwinding the double stranded DNA
- The required energy for this comes from the hydrolysis of ATP.
| --- | - 1x standard reaction buffer
| - To unwind the double stranded DNA
- TO unwind the DNA-RNA hybrid
- For some specific kind of PCR reaction
|
| Topoisomerase type I | - It controls and alters the topologic states of DNA during transcription.
- It catalyzes the transient breaking and rejoining of a single stranded DNA which leads to the rotation of the broken strand, thus altering the topology of DNA.
| --- | | - For the changing of topological states it is used
- No important use in biotechnology
|
| Topoisomerase type II | - It cuts both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to check DNA tangles and supercoils.
- They use the hydrolysis of ATP as a source of energy
- This is commonly known as gyrase and used in DNA replication for releasing the supercoiling of the DNA strand.
| --- | | For unwinding the DNA suoercoiling it is used. |
| Restriction enzymes | - These are enzymes used to cut the DNA or RNA strands from the restriction sites that are present in the perticular strand
- Each DNA have perticular sequence to which these enzymes bind and cut that nucleotides. These sequence containing sites are called restriction sites.
| S-Adenosyl methionine (AdoMet), hydrolyzed ATP, Mg2+ , | Typically standard restriction enzyme buffers which are different for different enzymes. | - Insertion of genes into plasmid vectors in the process of gene coding and protien purification.
- DNA fingerprinting
- To digest DNA for the souther blot analysis.
- Gene sequencing
|
 Homework Sourse
Homework Sourse